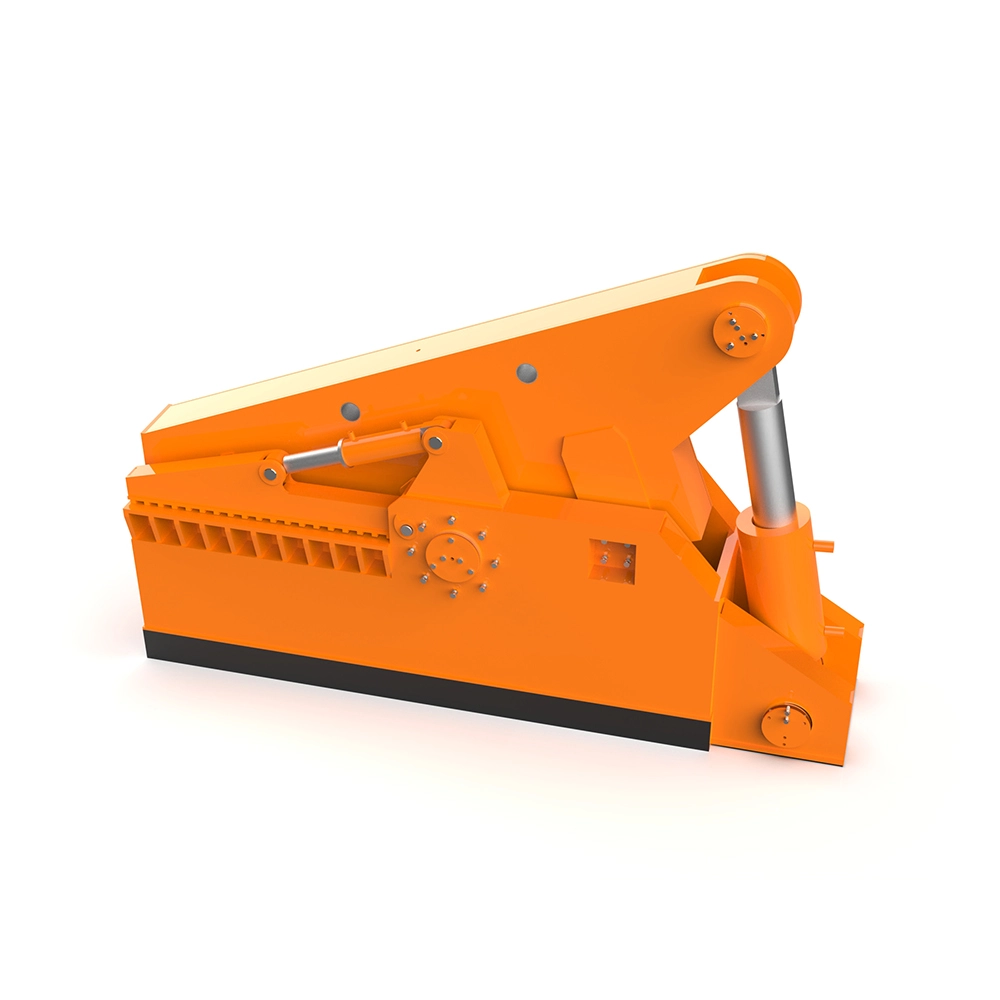
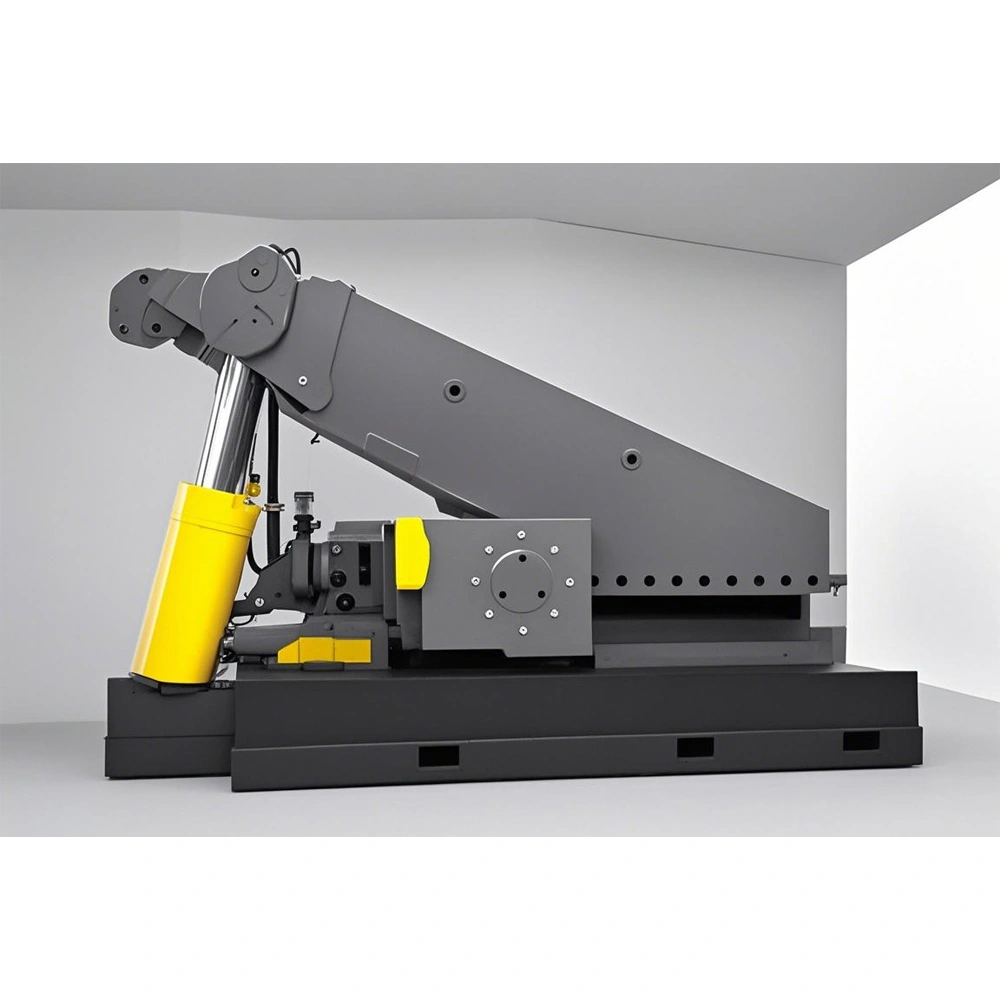
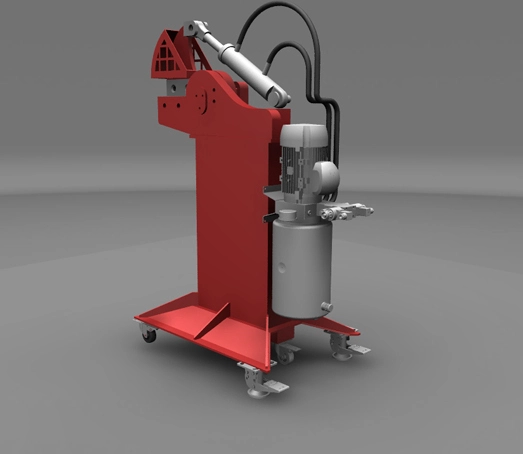
Advantages of Heavy Alligator Shear
1. Precision selection of high-strength blades
The blade of crocodile shear adopts high-strength tempered steel (such as 42CrMo and other special alloys), and forms a dense and uniform martensitic structure through multiple heat treatment processes (quenching + tempering), and the hardness can reach HRC55-60. This material not only has excellent wear resistance, can cope with the continuous cutting of high hardness metals (such as stainless steel, titanium alloy), but also by optimizing the carbide distribution, effectively resist the edge crack and plastic deformation. The blade has a four-sided reversible structure, which can be rotated when one side is worn, significantly extending the service life and reducing the replacement frequency.
2. Seismic and stability of cast iron fuselage
The body of the fuselage is made of high-strength cast iron, whose graphite form has been optimized to combine the shock absorption characteristics of cast iron with the tensile strength of steel. This material can effectively disperse the impact force generated during cutting, reduce the vibration of the equipment, and ensure the stability of long-term operation. At the same time, the corrosion resistance of cast iron is better than that of ordinary steel, and it is especially suitable for metal recovery operations in wet or corrosive environments.
3. Material compatibility of hydraulic system
The hydraulic cylinder and pipeline are made of seamless steel pipe, the inner wall is honed, the surface roughness Ra≤0.4μm, to ensure the smooth flow of hydraulic oil and reliable sealing. The piston rod surface is plated with chromium (thickness ≥20μm) to form a dense oxide film, which effectively resists the scratching of metal debris and liquid corrosion, and extends the service life of hydraulic components.

Applications of Heavy Alligator Shear
1. Metal recycling and scrap metal disposal
Scrap/scrap cutting: Cutting large pieces of scrap metal (such as used auto parts, construction steel, industrial equipment remains) into small pieces for easy transportation and smelting.
Non-ferrous metal treatment: Cutting aluminum, copper, zinc and other waste to improve recycling efficiency.
2. Car disassembly and recycling
Frame and body cutting: cutting the car chassis, engine support and other high-strength structural parts.
Metal parts separation: disassemble transmission, axle and other parts, separate recyclable metal.
3. Construction and demolition industry
Reinforced concrete treatment: Cut steel bars, I-beams and other metal structures in abandoned buildings.
Scrap removal: Quickly dispose of dismantled metal scrap to improve site efficiency.
Waste pipe cutting: the treatment of metal pipes and pipe fittings left in the building.
4. Manufacturing and metal processing
Blanking and forming: cutting sheet metal and bar in the manufacturing process for subsequent processing.
Scrap disposal: Recycle metal scraps from production to reduce material costs.
Special material cutting: suitable for stainless steel, alloy and other high strength materials.

 English
English 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 français
français tiếng việt
tiếng việt Indonesia
Indonesia Español
Español العربية
العربية русский
русский